Clinical benefits
Minimally disruptive surgery. Reproducible technique.
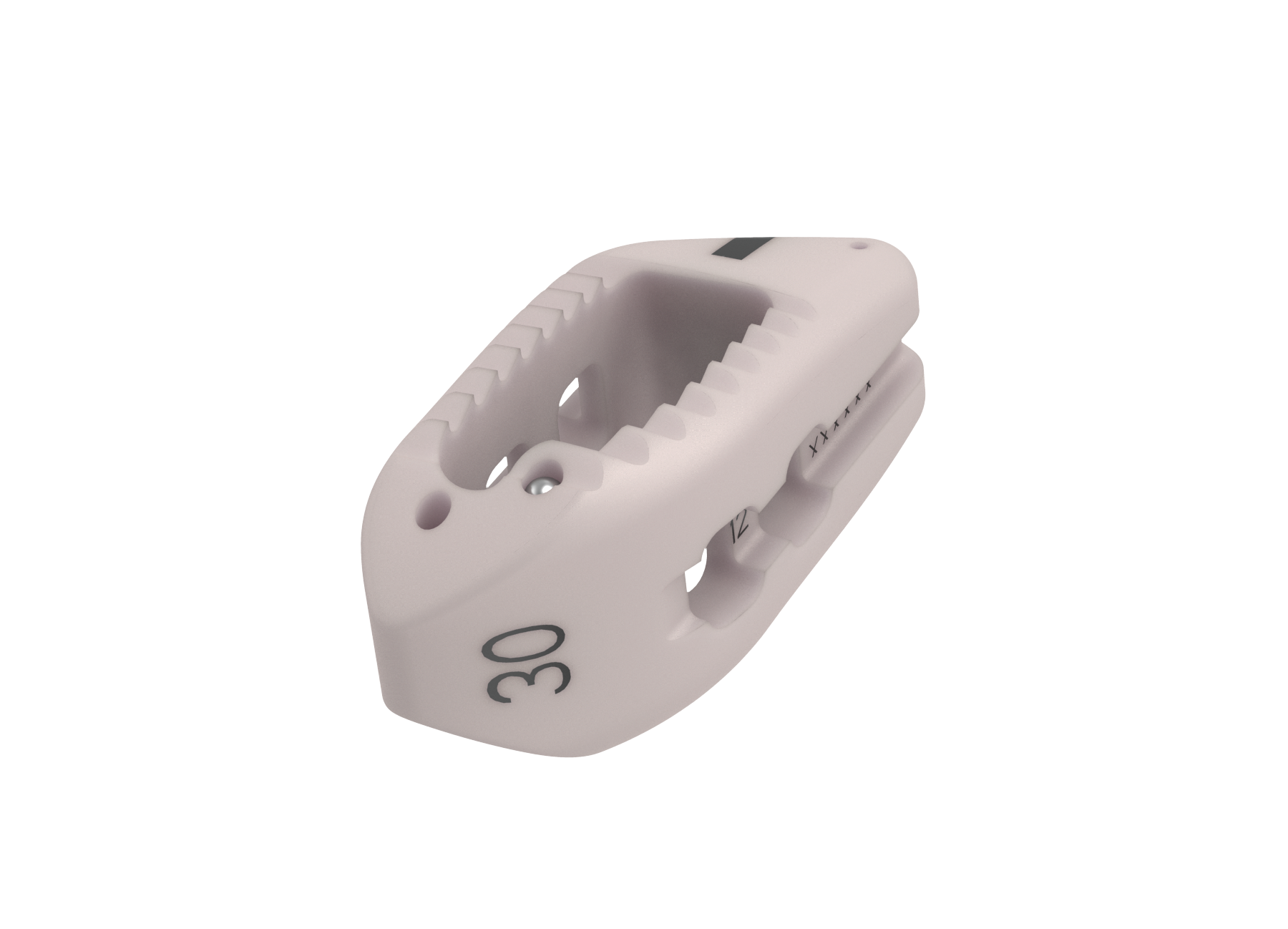
MAS® TLIF is an efficient and reproducible technique that offers the same advantages as traditional TLIF, but with the added benefit of less tissue disruption and therefore potentially less postoperative pain and quicker recovery. The pedicle-based retractor facilitates maximum visualization and access to anatomy via modular screw construct.
The MAS® TLIF integrated technologies provide a complete procedural solution encompassing access, interbody, fixation, biologics, and computer assisted surgery.